EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE
The atmosphere is a thick gaseous envelope that surrounds the earth and extends thousands of kilometers above the earth’s surface. Much of the life on the earth exists because of the atmosphere otherwise the earth would have been barren. In fact, the atmosphere directly or indirectly influences the vegetation pattern, soil type and topography of the earth.
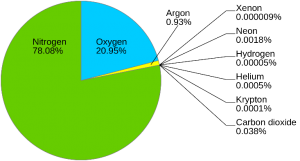
Composition of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is a mixture of several gases. It contains huge amount of solid and liquid particles collectively known as aerosols. Pure dry air consists mainly of Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, Carbon Dioxide, Hydrogen, Helium and Ozone. Besides, water vapour, dust particles, smoke, salts, etc. are also present in the air in varying quantities.
The chemical composition of atmosphere up to an altitude of about 90 km is uniform in terms of major gases-Nitrogen and Oxygen. This layer is called Homosphere. Above 90 km, the proportion of the gases changes with progressive increase in the proportion of lighter gases. This layer is known as Heterosphere. Nitrogen and Oxygen comprise 99% of the total volume of the atmosphere. But Nitrogen does not easily enter into chemical union with other substances.
It serves mainly as an agent of dilution and remains chemically inactive. Oxygen combines with all the elements easily and is most combustible. Carbon dioxide constitutes a small percentage of the atmosphere. It can cause the lower atmosphere to be warmed up by absorbing heat from the incoming short wave solar radiation from the sun and reflecting the long wave terrestrial radiation back to the earth’s surface.
Carbon dioxide is utilized by the green plants in the process of photosynthesis. Water vapour and dust particles are the important variables of weather and climate. They are the source of all forms of condensation and principal absorbers of heat received from the sun and radiated from the earth. Water vapour comprises 3-4% of the total volume of air.
However, the amount of water vapour present in the atmosphere decreases from the equator towards the poles. Nearly 90% of the total water vapour lies below 6 km of the atmosphere.
Structure of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere consists of almost concentric layers of air with varying density and temperature.

a) Troposphere:
- Lowest layer of the atmosphere
- The height of troposphere is 16 km thick over the equator and 10 km thick at the poles.
- All weather phenomena are confined to troposphere (e.g. fog, cloud, frost, rainfall, storms, etc.)
- Temperature decreases with height in this layer roughly at the rate of 6.5° per 1000 metres, which is called normal lapse rate.
- Upper limit of the troposphere is called tropopause which is about 1.5 km.
b) Stratosphere:
- The stratosphere is more or less devoid of major weather phenomenon but there is circulation of feeble winds and cirrus cloud in the lower stratosphere.
- Jet aircrafts fly through the lower stratosphere because it provides conducive flying conditions.
- Ozone layer lies within the stratosphere mostly at the altitude of 15 to 35 km above earth’s surface.
- Ozone layer acts as a protective cover as it absorbs ultra-voilet rays of solar radiation.
- Depletion of ozone may result in rise of temperature of ground surface and lower atmosphere.
- Temperature rises from -60°C at the base of the stratosphere to its upper boundary as it absorbs ultra-voilet rays.
- Upper limit of the Stratosphere is called stratopause.
c) Mesosphere
- Mesosphere extends to the height of 50- 90 km.
- Temperature decreases with height. It reaches a minimum of -80°C at an altitude of 80-90 km
- The upper limit is called mesopause.
d) Thermosphere
- It lies at 80 km to 640 km above the earth’s surface.
- It is also known as ionosphere.
- Temperature increases rapidly with increasing height.
- It is an electrically charged layer. This layer is produced due to interaction of solar radiation and the chemicals present, thus disappears with the sunset.
- There are a number of layers in thermosphere e.g. D-layer, E-layer, Flayer and G-layer.
- Radio waves transmitted from earth are reflected back to the earth by these layers.
e) Exosphere
- This is the uppermost layer of the atmosphere extending beyond the ionosphere.
- The density is very low and temperature becomes 5568°C.
- This layer merges with the outer space.



